Factoring
Zero Product Property
A quadratic equation is in factored form when it is rewritten as the product of two linear expressions. In general, the factored form of a quadratic is written as y = (x - R1) (x- R2) where R is equal to the roots of the equation. The Zero Product Property is then used to determine the solutions.
The Zero Product Property states if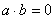 , then either a = 0 or b = 0. This is particularly useful when solving quadratic equations.
, then either a = 0 or b = 0. This is particularly useful when solving quadratic equations.
Example Solve the equation (x + 5)(x - 4) = 0.
The Zero Product Property states if
Example Solve the equation (x + 5)(x - 4) = 0.
Step 1. Use the Zero Product Property to set up two equations.
Since (x + 5)(x - 4) = 0, either x + 5 = 0 or x - 4 = 0.
Step 2. Solve each equation.
x = -5 or x = 4
*Note: x = -5 or 4 are the roots of the equation and the x -intercepts of the graph.